

Did you know that 45% of new businesses fail within the first 5 years? (US Bureau of Labor Statistics) It’s not because they lack potential but because they fail to track the right business metrics. Due to the lack of clear data, business owners rely on guesswork instead of data-driven insights, resulting in missed opportunities and costly mistakes.
However, by understanding and tracking the right data like employee hours, net income, and return on investment, you can optimize strategies, improve efficiency, and make smarter business decisions.
In this blog, we will explore the 37 crucial business metrics that every organization must track to boost growth and ensure long-term success, along with expert insights on how to track business metrics efficiently.
| Quick Summary Business metrics are critical for evaluating a company’s success and guiding strategic decisions. In this comprehensive guide, we cover 37 essential business metrics to track, from financial and sales metrics to customer and human resources insights. Learn how to choose the right metrics for your business, why tracking them is essential, and the best tools to help you monitor progress in real time. Stay ahead of the competition with actionable insights that lead to informed, data-driven decisions. In this blog, you’ll discover: ⦿ Tips on how to avoid vanity metrics and focus on meaningful data ⦿ 37 key business metrics for financials, sales, customer satisfaction, HR, and more ⦿ How to select the right metrics based on your business goals ⦿ Why tracking metrics is essential for improving performance and ROI ⦿ The best tools and software to track and analyze business metrics effectively |
But, before we dive into business success metrics, let’s first understand what business metrics are.
Business metrics are measurable indicators that help business owners track and analyze the company’s performance across different areas like finance, sales, marketing, and customer satisfaction. These metrics provide valuable insights into business operations, helping companies make informed decisions, set goals, and optimize strategies for success.
By tracking the key business performance metrics, you can spot growth opportunities, address challenges effectively, and stay ahead of competitors in the fast-evolving market.
Tracking the right business metrics is essential for measuring business performance and improving operational efficiency. These metrics not only help business owners and entrepreneurs but also allow teams to evaluate processes, identify areas of improvement, and optimize strategies to drive growth.
Here are the 37 essential business success metrics that will help you make data-driven decisions and fuel business success.
Financial metrics are measurable numbers that provide insights into a company’s financial performance. According to a study by US Bank, 82% of businesses fail due to cash flow issues and poor financial management. This highlights the benefits of tracking metrics like gross profit margin, net income, and ROI, which provide a clear picture of profitability, expenses, and overall financial health. By monitoring these performance metrics, businesses can make smarter decisions, prevent financial setbacks, and build a foundation for long-term growth.
Gross profit margin is the percentage of the company’s revenue that remains after deducting the direct expenses such as labour and materials. It helps businesses allocate resources wisely by identifying the most profitable products and ultimately optimizing investments.

Suppose a bakery generates a revenue of $50,000. The direct costs of ingredients and labor (COGS) are $20,000. Its Gross Profit Margin = (($50,000 – $20,000) / $50,000) x 100, or 60%.
A trending question among new business owners is “What is net income?” Net income is the total amount a business earns after subtracting all the expenses, such as cost of goods sold (COGS), interest on debt, taxes, operating expenses, depreciation, and amortization.

Understanding net income is crucial as it reflects a company’s actual profitability, helping businesses assess financial health, attract investors, and make strategic decisions.
Net profit margin is the percentage of profit a business produces from its revenue after deducting all the expenses, such as taxes, operating costs, interests, and COGS (Cost of goods sold). It is one of the most important key performance indicators (KPIs) because it shows a company’s overall profitability and financial health.

Return on Investment(ROI) is one of the most important business metrics that measures how profitable an investment is compared to its cost. It’s a crucial tool for evaluating potential returns before investing in stocks, startups, or new business ventures, enabling smart financial decisions.

For instance, A company invested $5,000 in a social media campaign that generated $15,000 in sales. Their ROI is [($15,000 – $5,000) / $5,000] * 100 = 200%. This means for every dollar invested, they earned two dollars in return.
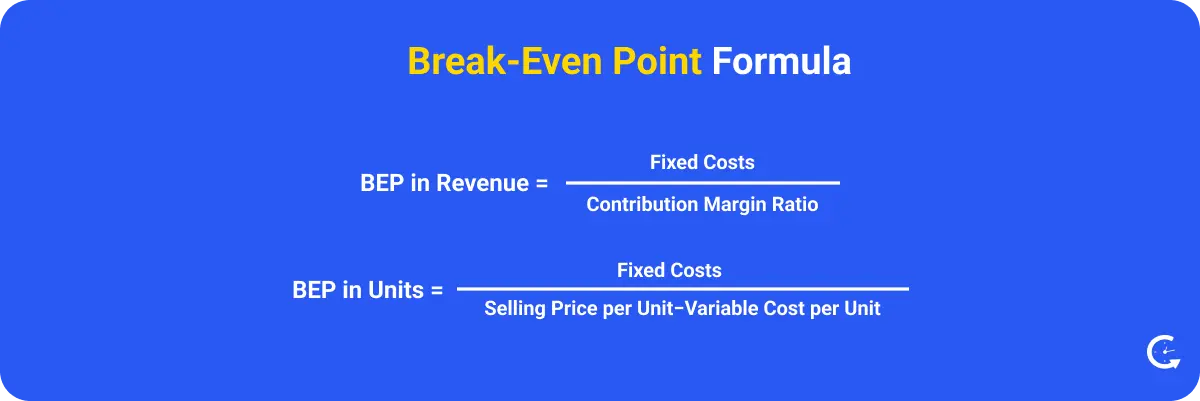
The break-even point is when a company’s total revenue is exactly equal to its total expenses, meaning there is no profit or loss. It is a critical business metric for businesses as it helps them calculate how much they need to sell before they start making a profit.
But why is this number so important? For startups, it’s like a roadmap – telling you how much you need to sell to start seeing a profit. For established businesses, it’s a health check, showing you how changes in pricing or costs can impact your bottom line. You can measure the break-even point in the number of units you need to sell, or in total revenue dollars.
Operating cash flow is the amount of money a company generates from its day-to-day business operations over a specific period. It is one of the most crucial small business success metrics that shows whether a company can sustain and expand operations without relying on external financing.

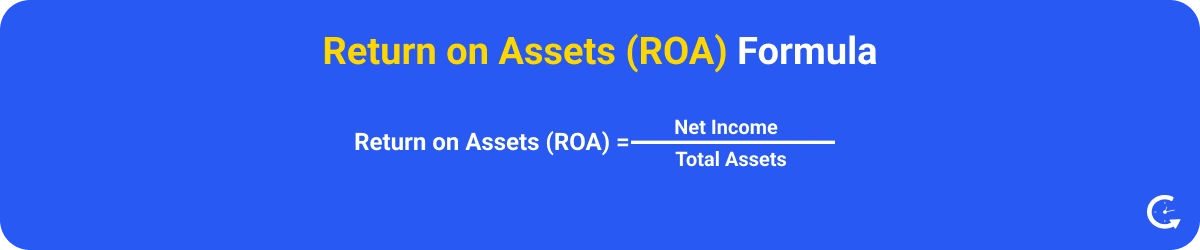
Return on assets is a metric that measures how well a company uses its assets to generate a profit. A higher ROA means the company is more efficient at using its assets to make a profit, while a lower ROA shows underutilized assets. It’s a key metric for evaluating the operational efficiency and financial performance of a company.
Sales and Revenue metrics play a crucial role in evaluating a company’s ability to generate income. A McKinsey survey found that companies using business metrics and KPIs in decision-making experience 16% higher revenue growth. This shows how essential tracking sales and revenue metrics is, not only to understand the current performance but also to uncover valuable insights, spot growth opportunities, and make smarter decisions that drive long-term profitability.
Monthly recurring revenue measures the predictable revenue that a company expects to generate from its customers every month for offering a product or service. It is a key financial metric for SaaS (Software as a service) based companies and subscription-based companies.
By analyzing MRR, businesses can spot growth opportunities, forecast future income, and make strategic decisions.

Types of MRR
MRR can be further divided into various components that reveal how your recurring revenue is earned:
Churned MRR: The revenue lost when customers cancel their subscriptions.
Customer lifetime value (CLV) is a key metric that measures the total revenue a business can expect from a customer throughout the time they remain a customer. By knowing the potential revenue from each customer, companies can enhance marketing strategies, personalize customer experiences, and optimize marketing budgets.

For example, a video streaming platform calculates that the average subscriber stays for 3 years, paying $15 per month. Their CLV is $15/month x 36 months = $540. This helps them justify acquisition costs up to that amount.
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) is the total amount of money a business spends on acquiring a new customer. By calculating the total cost of acquiring a new customer, including marketing, sales, and advertising expenses, businesses can assess the effectiveness of their strategies and make informed decisions to drive growth.

Consider this example: A restaurant spent $1,500 on local advertising and promotions and attracted 150 new customers. Their CAC is $1,500 / 150 customers = $10 per customer. This shows a relatively low acquisition cost, which is common for local businesses.
Net sales are the total revenue a company earns from selling its products or services, excluding any returns, allowances, and discounts. This number gives a clear picture of the company’s financial performance and profitability, making it a key metric for measuring growth.

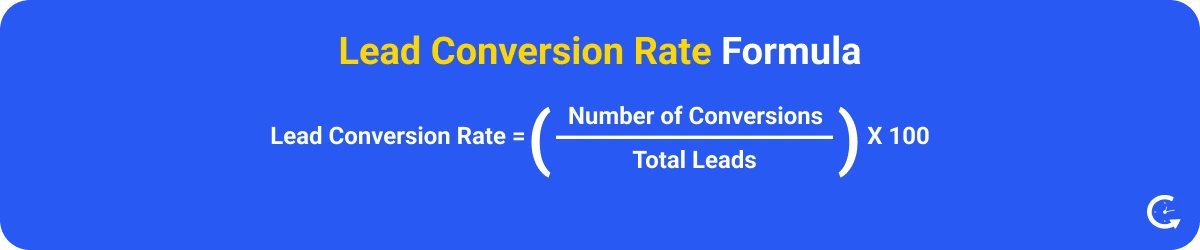
Lead conversion rate is the percentage of leads that successfully turn into paying customers. By measuring this, businesses can assess the effectiveness of their sales and marketing strategies, where a high rate indicates strong lead nurturing and sales processes.
The customer churn rate is the percentage of customers who stop using a business’s services over a specific period of time. Monitoring this business metric is essential, as lowering the churn rate can significantly boost customer retention, profitability, and brand loyalty.

Total new customers are the number of new customers acquired by a business over a specific period. It directly reflects business growth and the performance of sales and marketing strategies.
Revenue growth rate is the percentage increase in a company’s revenue over a period. It is a key metric to measure success, allowing businesses to evaluate their expansion and financial health.

For instance, if a company’s revenue increased from $100,000 to $120,000 in a quarter, the revenue growth rate will be [($120,000 – $100,000) / $100,000] * 100 = 20%. This shows a 20% increase in revenue for that quarter, indicating positive business growth.
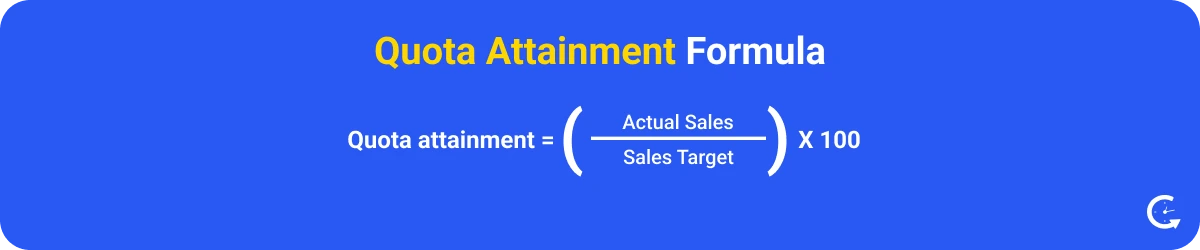
Quota attainment is the percentage of a sales representative’s target that they have achieved. It is a key performance indicator for assessing sales efficiency and goal achievement.
By integrating sales performance metrics examples, such as quota attainment, into sales evaluations, businesses can identify top performers, optimize incentive structures, and refine sales strategies for increased efficiency.
Customer satisfaction and loyalty can directly impact your business’s bottom line. A study in The Australian found a 90% correlation between brand preference and sales, while data-driven companies are 3x more successful than those without strong data practices. By analyzing customer metrics, businesses can gain insights into customer behavior, improve satisfaction, and enhance loyalty, all of which contribute directly to increased sales and long-term success.
Net Promoter Score is a metric that measures how likely customers are to recommend your service or business on a scale of 0 to 10. This rating classifies customers as detractors (0-6), passives (7-8), or promoters (9-10).

The Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT) is used to measure customer satisfaction based on their experience with a product or service. By tracking this business metric, organizations can improve their offerings and address customer concerns effectively.
Companies typically measure customer satisfaction by asking a follow-up question like: ‘On a scale of 1 to 10, how satisfied were you with the experience?’ (1 = extremely unhappy, 10 = extremely happy). By calculating the average of customer responses, a customer satisfaction value is obtained. This value, where higher numbers signify greater satisfaction and a smaller number informs businesses on addressing potential issues and reinforcing effective practices.
One of the benefits of tracking metrics stats as CSAT is that businesses can quickly pinpoint pain points in the customer journey and make data-driven improvements, leading to better customer retention and brand loyalty.
Customer retention rate is the percentage of customers a company keeps over time, directly reflecting customer loyalty and business stability.

For instance, if a subscription service starts with 1,000 customers and retains 900 after a year, their retention rate is 90%, signaling strong loyalty and a stable customer base.
Customer complaint resolution time is the average time a business takes to resolve customer complaints. This includes the time spent acknowledging the complaint, investigating the issue, and providing a resolution.
By monitoring this business metric, businesses can identify bottlenecks in their customer service process. Faster resolution times directly enhance customer satisfaction and retention, making it a critical performance metric.
Companies that effectively track and analyze marketing metrics achieve remarkable growth by transforming raw campaign data into actionable insights. For example, JLL, a global real estate firm, saw a threefold increase in pipeline contribution and a 4x increase in revenue contribution, all while using 11% fewer resources and enhancing overall effectiveness by over 20% They accomplished this by developing 16 KPIs to track everything from pipeline contribution and revenue impact to digital engagement, campaign effectiveness, and marketing ROI.
By leveraging data-driven insights, businesses can fine-tune strategies, optimize spending, and maximize results, ensuring every marketing effort contributes to measurable success.
Cost Per Lead (CPL) is a crucial business performance metric that measures the cost of acquiring a single lead through marketing efforts. It is essential to understand your CPL for evaluating the efficiency of your marketing campaigns and optimizing your budget.
For example, a lower CPL indicates a more effective marketing strategy.

ROMI is a key marketing metric that helps businesses evaluate the profitability of their marketing campaigns. By using this metric, businesses can make data-driven decisions and allocate marketing budgets more effectively to maximize returns.

For example, you spend $8,000 on an influencer campaign, resulting in $40,000 in sales at a 25% margin, contributing $10,000 to profit, which has a ROMI of ((40,000 x 0.25) – 8,000) / 8,000 x 100 = 25%.
To assess the effectiveness of your website content and user experience, businesses track Bounce Rate. It is the percentage of visitors who leave a website without interacting.

If a website has 10,000 visitors and only 1,000 bounce after viewing the first page, the bounce rate is (1,000 / 10,000) x 100, or 10%, which is excellent. A low bounce rate like this example signals that the content resonates with customers, leading to improved user retention and website performance.
Conversion rate is a crucial performance metric that measures the percentage of website visitors or leads who complete a desired action, such as purchase or signup. This metric is vital for evaluating the effectiveness of sales and marketing efforts, directly impacting overall business success.

For example, if an e-commerce site has 1,000 visitors and 50 make a purchase, the conversion rate is (50 / 1,000) x 100 = 5%.
Email Open and Click-through Rates are the percentage of recipients who open emails and engage with the content, such as clicking on links.

For instance, an email campaign with a 30% open rate and a 10% click-through rate demonstrates effective email marketing strategies. Tracking these quantitative metrics is essential for optimizing email campaigns and improving customer engagement.
Social Media Engagement tracks interactions like likes, shares, and comments on social media platforms. It reflects audience interest, brand awareness, and the effectiveness of your content strategy.
Brand awareness measures how well customers recognize and recall a business. Strong brand recognition leads to enhanced customer trust and sales growth.
For instance, a survey showing 70% of respondents recognize a company’s logo indicates high brand awareness.
HR metrics help businesses turn workforce data into valuable insights. They measure employee productivity, hiring success, and overall satisfaction. These key performance indicators (KPIs) empower organizations to improve processes, boost engagement, and build a strong, motivated workforce that drives business success.
Employee turnover rate calculates the percentage of employees who leave a company within a given period. Losing employees is normal for every company, but a high turnover number can indicate workplace problems and dissatisfaction.
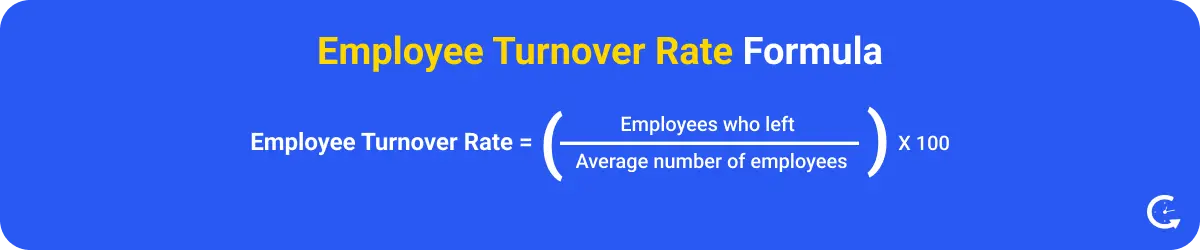
For instance, losing top performers is far more damaging than losing underperformers, even if overall numbers are low. Tracking both voluntary and involuntary exits, especially among high performers, provides a clearer view of true talent health and potential risks.
Cost per hire is a fundamental key performance indicator (KPI) that tracks all the expenses associated with recruiting and onboarding new employees. It helps businesses optimize hiring budgets and improve recruitment efficiency.

For instance, a tech company might spend $10,000 to hire a senior software engineer who leads key projects and mentors others, making it a worthwhile investment. But if they spend $5,000 on a junior developer who quits in six months, it’s a loss. By tracking CPH and how well new hires do, companies can make smarter hiring decisions and get the best value for their money.
Time to fill measures the average time taken to fill a job vacancy, but it’s more than just a timeline. It shows the efficiency of your recruitment process and its impact on overall costs.
For example, reducing Time to Fill by 10 days for high-demand roles can significantly lower recruitment expenses and minimize lost productivity. By analyzing this business metric, organizations can streamline their hiring process, attract top talent faster, and gain a competitive edge in the talent market.
The absenteeism rate is the percentage of workdays missed by employees and serves as a critical indicator of overall workplace health and employee well-being. High rates can disrupt productivity, lower morale, and signal job dissatisfaction. By monitoring this business metric, businesses can address potential problems proactively and create a healthier work environment.

Consider this example: a company with 50 employees, each working 20 days a month, has 1,000 total workdays. If 80 of those days are missed, the absenteeism rate is (80 / 1,000) x 100 = 8%. This 8% rate indicates a significant loss of work time, suggesting possible workplace issues like burnout, poor engagement, or health problems.
Training Spend per Employee is an essential business metric that refers to the average amount of money a company invests in employee training and development. While training enhances skills and improves efficiency, its true value comes from the return on investment- helping employees perform better and contribute more to the company’s success.

For example, if a company invests $5,000 per employee in specialized software training, and that training leads to a 20% increase in project completion rates and a 10% reduction in errors, this shows a clear return on the training investment. Tracking this metric allows businesses to determine if training truly enhances productivity and drives profitability.
Diversity and inclusion KPIs measure the workforce diversity within the company and ensure equal opportunities to foster a positive workplace culture where everyone feels valued, respected, and empowered. By focusing on these business success metrics, you can create a more inclusive and successful company.
Performance ratings provide a clear way to evaluate employee performance based on key performance indicators (KPIs). They help identify top talent, highlight areas for growth, and ensure employees get the support they need. When used effectively, they foster development, boost engagement, and drive long-term business success.

Employee satisfaction surveys provide real insights into how your employees feel about their work. They offer a data-driven approach to measure employee morale and job satisfaction.
When employees are happy, they’re more productive and less likely to leave the job, which benefits your business. However, these surveys are not just about keeping the employees satisfied but also about creating a positive workplace culture that attracts and retains top talent.
HR Budget vs. Actual Spending is a key business success metric that compares planned HR expenses with actual spending. This helps identify spending patterns, optimize resources, and find cost-saving opportunities, improving HR’s impact on the business.
Revenue per employee is an important HR metric that calculates the average revenue generated per employee. A higher number means a more efficient workforce and better use of resources, which directly boosts profitability. It’s a great way to evaluate overall productivity and business performance.

For instance, if a company with 50 employees generates $5 million in revenue, the revenue per employee is $100,000.
When it comes to choosing the right key business metrics, your focus should be on metrics that align with your business goals, provide useful insights, and help you make better decisions. Selecting the right business success metrics will give you clarity, guide strategic decisions, and highlight areas for growth.
On the other hand, tracking irrelevant KPIs and metrics can lead to wasted time, misleading insights, and missed opportunities. This raises an important question: how to create business metrics? Here are key steps to help you choose and implement the best metrics for your business.
Start by defining your primary business goals or what exactly you are trying to achieve. By getting a clear view of your goals, you will be able to determine which performance metrics will provide the real value.
The right business metrics can make all the difference in driving success, but tracking too many can lead to confusion. Instead of monitoring every possible key metric, narrow them down to a selected few that have a real impact on your business. By narrowing your focus to the most meaningful business success metrics, you’ll gain clearer insights, make smarter decisions, and drive real progress for your business.
Business metrics should do more than just track numbers, they should guide your decisions and drive real improvements. If you’re keeping an eye on website traffic but not digging into where visitors drop off, that data won’t be helpful. Instead, focus on business performance metrics that highlight problems and opportunities, so you can take action.
Every industry has its own set of benchmarks for success. Comparing your numbers to industry averages can help you get a clearer view of how your business is performing and where improvements are required.
Some metrics and KPIs predict future trends, while others reflect past results. Lagging indicators, like revenue and profit, show how your business has performed in the past, while leading indicators help predict future success.
For example, website traffic can indicate future sales (leading), while revenue confirms past performance (lagging). By tracking a balance of both, you gain a complete picture of your business health, helping you make proactive and informed decisions.
As your business grows and evolves, so should the success metrics you track. It is crucial to review your business metrics regularly and check if they still align with your goals. If a metric doesn’t offer valuable insights or drive better decisions, replace it with a more impactful metric.
Many businesses fall into the trap of selecting performance metrics that look impressive on paper, but don’t necessarily add any real value to their business growth. For example, social media likes or email subscriber counts may seem significant, but if they are not leading to real sales or engagement, they hold little value. Instead of focusing on vanity metrics, prioritize tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) that directly impact revenue, operational efficiency, and customer satisfaction.
With the ever-increasing competition in the business landscape, tracking the right metrics is more crucial than ever. Tracking business metrics isn’t just about numbers; it’s about making smarter decisions, improving performance, and staying competitive. If you are not tracking business success metrics, you are missing out on growth opportunities and critical insights that drive measurable success. Here’s why tracking KPIs and metrics is essential:
Without clear insights, businesses rely on assumptions, which can lead to costly mistakes. By tracking key business metrics that provide valuable insights allow companies to make informed choices backed by data.
One of the main benefits of tracking metrics is that it offers a reliable way to evaluate business performance over time. Whether it’s monitoring sales revenue, measuring employee productivity, or assessing customer satisfaction, these business success metrics provide valuable insights. By consistently tracking them, businesses can identify what’s working well and identify areas that need improvement to drive long-term success.
Business metrics play an important role in ensuring that every department stays aligned with the company’s overall objectives. When teams consistently track business success metrics, they remain focused on measurable outcomes that contribute to business success.
Every business has limited resources, whether it’s budget, talent, or time. By keeping an eye on cost-related metrics like Cost Per Hire (CPH) or Return on Investment (ROI), companies can make smarter financial decisions, ensuring all the money is spent in a way that drives growth and efficiency.
Tracking key efficiency metrics, such as employee productivity and operational costs, helps businesses fine-tune their operations and minimize disruptions. By focusing on these insights, companies can optimize resources, improve processes, and enhance productivity.
Comparing your business performance metrics to industry benchmarks gives you a competitive edge. If your conversion rate falls below the industry average, it’s a clear signal that there’s a need for improvement. By closely analyzing competitor performance and market trends, businesses can refine their strategies, improve their products, and strengthen their overall market position.
Metrics help highlight both growth opportunities and areas that need attention. For instance, if the data shows that a particular product line is generating the highest profit margins, businesses can focus more on promoting it. Similarly, tracking customer success KPIs like churn rate can help pinpoint potential service issues early, allowing companies to fix them before they negatively impact overall business performance.
Without the right tools, tracking business metrics can be challenging. But when you have the right tools in place, you can easily collect data, gain real-time insights, and make better decisions. Below are some of the best tools and software that can help you track key business metrics effectively.
Business intelligence (BI) tools help turn raw data into actionable insights. With platforms like Google Analytics, Tableau, and Power BI, you can effortlessly analyze trends, measure performance, and make data-driven decisions. These tools allow you to:
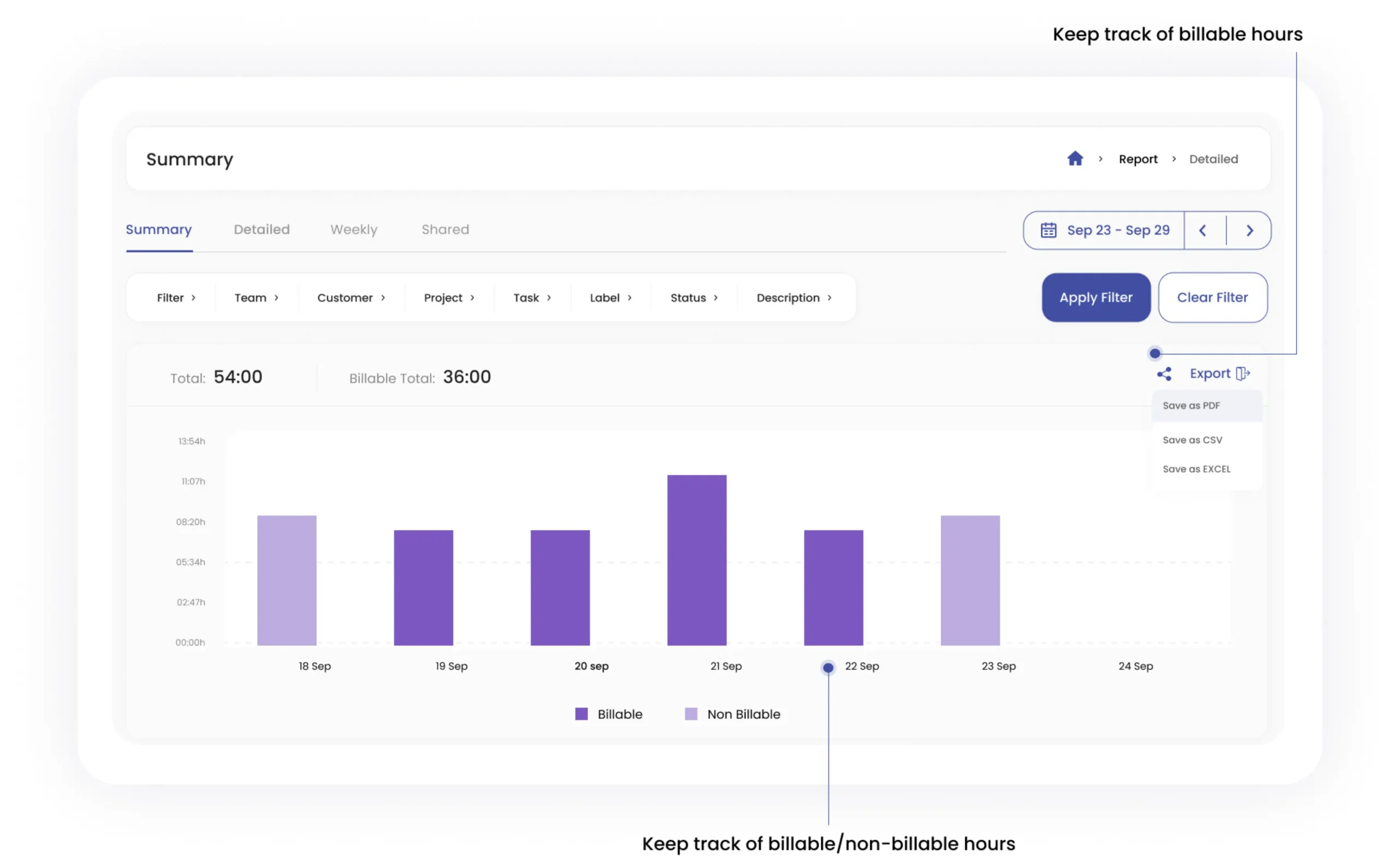
A centralized business metrics dashboard ensures you always have key data at your fingertips. Tools like Google Data Studio and Databox allow you to visualize different business metrics in real time. By integrating data from multiple sources, businesses can quickly assess progress and respond to trends.
Monitoring employee productivity is essential for operational efficiency. Smart time-tracking tools like Clockdiary help businesses measure time spent on tasks, track billable hours, and improve workflow efficiency. These tools provide insights into workforce performance, helping teams optimize time management and productivity.
Conclusion
In today’s competitive business landscape, tracking the right metrics is no longer an option but a necessity. By monitoring business metrics, organizations can make data-driven decisions, optimize operations, and stay on top of industry trends.
By leveraging time-tracking tools like Clockdiary, businesses can simplify productivity tracking, making it easier to manage time efficiently and boost overall performance. With the right insights at your fingertips, you can make smarter business decisions, streamline processes, and drive long-term success.

Frequently Asked Questions
Ans: To measure success in the workplace, focus on measuring metrics and key performance metrics (KPIs) aligned with your goals. Track business metrics like productivity using time tracking tools such as Clockdiary, sales, customer satisfaction, and employee performance reviews. These business success measures allow companies to ensure they are on track toward meeting their objectives and achieving long-term growth.
Ans: Business metrics are important because they help companies track performance, measure progress toward goals, and guide data-driven decision-making. By analyzing these metrics, businesses can identify business success factors and optimize operations. These insights into business processes and company performance allow businesses to identify opportunities, address challenges, and stay competitive.
Ans: You can measure the success of a business by using key metrics such as revenue, profit margins, net revenue, cost per lead, and more. Tracking these business success metrics helps evaluate financial health, operational efficiency, and overall growth. The right success indicators depend on the business’s goals and industry.
Here are some business performance metrics examples: gross profit margin, conversion rate, and employee productivity that can help evaluate productivity, track progress, and identify areas for improvement.
Ans: To create business metrics, follow these steps:
1. Define Clear Business Goals – Start by identifying what you want to achieve.
2. Select the Most Relevant KPIs – Focus on key metrics that truly impact success.
3. Track Meaningful Data – Track data that leads to meaningful decisions.
4. Use Industry Benchmarks – Compare your performance against industry standards.
5. Monitor Leading & Lagging Indicators – Balance past performance with future predictions.
6. Regularly Review Your Metrics – Ensure that your business metrics stay relevant as your business evolves.
Ans: Key performance indicators in business are measurable values that help you track how well your business is achieving its goals. They provide insights into financial growth, customer satisfaction, employee productivity, and efficiency. By regularly analyzing KPIs, companies can assess their performance, spot areas that need improvement, and make data-driven decisions for better outcomes.