

Ever wondered how much of your team’s potential is truly being harnessed? Recent studies reveal that the average employee is productive for only about 2 hours and 53 minutes in an 8-hour workday. This startling statistic underscores the critical need for leaders to accurately calculate productivity of an employee.
Here arises the burning question: how to measure productivity of an employee? By understanding precise metrics and implementing effective strategies, CEOs, managers, and team leaders can unlock unprecedented levels of efficiency within their organizations while improving work-life balance for employees as well.
| Quick Summary Understanding how to calculate employee productivity is essential for improving performance, maximizing output, and aligning team efforts with business goals. This guide walks you through proven methods, practical formulas, and step-by-step instructions for measuring productivity—both quantitatively and qualitatively. Whether you’re managing a remote team, running a professional service, or leading a manufacturing unit, this blog will help you track performance with clarity and precision. In this blog, you’ll discover: ⦿ What employee productivity means and why it matters for your business ⦿ 4 key formulas, including labor productivity formula and revenue per employee formula ⦿ Qualitative methods like 360-degree feedback and project-based evaluations ⦿ How to calculate employee productivity in Excel ⦿ Industry-specific examples for manufacturing, services, and remote teams ⦿ Key considerations when measuring productivity, from deadlines to output quality ⦿ Emerging trends like real-time tracking, AI tools, and continuous feedback ⦿ Why Clockdiary is a top solution for tracking, analyzing, and boosting productivity |
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the formulas, methods, and best practices to assess and boost your team’s productivity, ensuring your organization thrives in today’s competitive landscape. So, let’s begin.
Employee productivity measures how efficiently an employee completes tasks that contribute to business goals. It is typically quantified by output per unit of input, such as work completed per hour, revenue generated per employee, or task completion rates. A productivity calculator can come in handy here. A highly productive workforce directly impacts profitability, efficiency, and overall organizational success.
To get a holistic view of employee productivity, organizations should track multiple metrics:

By leveraging these metrics, businesses can make data-driven decisions to enhance employee productivity and overall organizational success.
Measuring employee productivity is extremely important for organizational success, as it helps identify areas for improvement and recognize high performance. But how to measure productivity of employees in service sector? Well, there are several methods and formulas that can be employed to calculate productivity effectively:
The fundamental productivity calculation involves dividing the total output by the total input:

Example: If a team produces 2,000 units in a month using 500 labor hours, the productivity calculation would be:
Productivity = 2000 Units / 500 Hours = 4 units per hour.
This simple formula provides a clear measure of how effectively resources are being converted into outputs.
Labor productivity focuses on the output generated per employee, offering insights into workforce efficiency:

Example: If a company produces 5,000 units in a quarter with 50 employees, the labor productivity would be:
Labor Productivity = 5000 units / 50 employees = 100 units per employee
This metric helps calculate productivity per employee, so that you can understand the average contribution of each employee to the organization’s output.
Multifactor productivity (MFP) provides a comprehensive view by considering multiple inputs, such as labor, capital, and materials. The Multifactor Productivity Formula goes something like this:
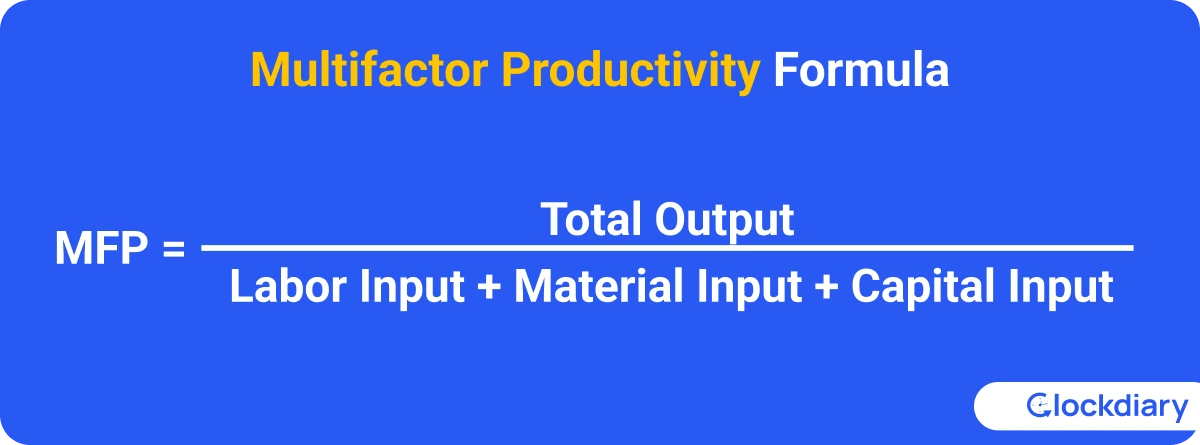
Example: An organization produces goods worth $10,000 using $2,000 in labor, $3,000 in materials, and $1,000 in capital:
MFP = $10000 / $2000 + $3000 + $1000 = $10000$6000 ≈ 1.67
A multifactor productivity of 1.67 indicates that for every dollar invested in inputs, the organization generates $1.67 in output. This comprehensive approach provides a holistic view of productivity by accounting for various resources.
Revenue per employee assesses the average revenue generated by each employee, reflecting the organization’s efficiency in utilizing its human resources:

Example: If a company reports annual revenue of $1,000,000 and employs 100 people, the revenue per employee would be:
Revenue Per Employee = 1,000,000 dollars / 100 employees = $10,000 per employee
This metric is valuable for comparing efficiency across organizations or industries. Also, having an idea of net vs. gross pay helps understand payroll expenses when calculating revenue per employee.
Each of these methods offers distinct insights into employee productivity. Selecting the appropriate productivity formula depends on the specific aspects of productivity an organization aims to measure, thereby ensuring a customized approach to performance assessment.
While traditional productivity formulas focus on numerical output, qualitative and alternative methods provide a deeper, more holistic understanding of an employee’s contributions. These approaches assess skills, collaboration, innovation, and overall work quality—factors that are crucial but often hard to quantify.
Below are three key methods to calculate productivity of an employee beyond numbers.
360-degree feedback is a comprehensive evaluation method that gathers insights from multiple sources, including managers, peers, subordinates, and even clients.
Instead of relying on a single perspective, this approach provides a well-rounded view of an employee’s performance, teamwork, leadership, and communication skills.
Why It Works:
Example:
A marketing manager may receive feedback from their direct reports on leadership skills, from peers on collaboration, and from senior management on strategic thinking. This multi-perspective assessment helps gauge their overall impact on the organization.
Encouraging employees to evaluate their own performance promotes self-awareness and accountability.
Self-assessments allow employees to reflect on their achievements, challenges, and personal growth over a period of time. Peer reviews complement this by offering constructive feedback from colleagues who closely observe day-to-day contributions.
Why It Works:
Example:
In a software development team, a developer might rate their own coding efficiency, problem-solving ability, and teamwork. At the same time, colleagues can provide input on collaboration, adaptability, and technical skills. This combined feedback helps paint a clearer picture of overall productivity.
For employees working on long-term or complex projects, assessing productivity based on project outcomes rather than daily task completion is often more effective. This method evaluates an individual’s role in a project, including problem-solving ability, innovation, and overall contribution to success.
Why it Works:
Example:
A project manager leading a product launch can be evaluated based on the project’s success—whether it met deadlines, stayed within budget, and achieved desired results. Instead of just measuring hours worked, the focus is on execution, leadership, and problem-solving.
Qualitative and alternative methods of measuring productivity provide a well-rounded approach to employee evaluation. While quantitative metrics are essential, they don’t always capture creativity, collaboration, or leadership skills. Combining traditional methods with these qualitative approaches ensures a more accurate and fair assessment of employee contributions.
Calculating employee productivity is essential for understanding how effectively your team converts inputs into valuable outputs. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you navigate this process:
Begin by identifying what constitutes ‘output’ in your organization. This can vary based on industry and role:
Clarifying these metrics ensures that productivity assessments align with organizational goals.
Next, identify the resources invested to achieve the outputs:
Accurately measuring these inputs is crucial for precise productivity calculations.
Since productivity can be measured in different ways, selecting the right method depends on the nature of the job and the business goals. Consider the following:
By choosing the most relevant approach, organizations can ensure their productivity assessments are meaningful and actionable.
Once you’ve calculated productivity of an employee, it’s time to derive actionable insights:
Microsoft Excel is a popular tool that enables organizations to calculate productivity of an employee and analyze it effectively and efficiently. By leveraging its functionalities, managers can track performance, identify trends, and make informed decisions.
Below is a comprehensive guide on how to calculate productivity of an employee in Excel, complete with examples and references to pre-built formulas and templates.
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how you can make use of Excel to calculate employee productivity effortlessly:
Begin by identifying the metrics that represent output (e.g., units produced, revenue generated) and input (e.g., hours worked, resources used). Clear definitions are crucial for accurate calculations.
Create a structured Excel worksheet to input your data:
Example:
| Employee Name | Units Produced | Hours Worked |
| John Doe | 500 | 40 |
| Jane Smith | 450 | 35 |
| Bob Johnson | 600 | 50 |
Use the Basic Productivity formula:
Productivity = Total outputTotal Input
In Excel, insert the following formula in Column D to calculate productivity for each employee: = B2/C2
Drag this formula down the column to apply it to all employees.
Updated Example:
| Employee Name | Units Produced | Hours Worked | Productivity (Units per Hour) |
| John Doe | 500 | 40 | 12.5 |
| Jane Smith | 450 | 35 | 12.86 |
| Bob Johnson | 600 | 50 | 12 |
With productivity calculated, you can:
To streamline productivity tracking, consider utilizing pre-built Excel templates and formulas:
This template allows you to monitor individual and team productivity over time. Features include:
Excel time-tracking templates for project hours can also come in handy here.
Excel offers functions that can enhance productivity analysis:
| =AVERAGEIF(D2:D10, “>0”) |
Steps:
Steps:
To ensure data integrity:
Steps:
By implementing these strategies, Excel becomes a powerful tool for calculating the productivity of an employee in the service sector and analyzing it meticulously, thereby facilitating data-driven decisions that enhance organizational performance.
Calculating productivity of an employee varies significantly across industries due to differing operational metrics and performance indicators. This raises the definite question: how to calculate employee productivity rates across varying industries?
Here, we will take a look at some industry-specific examples of productivity calculations in manufacturing, professional services, and remote work teams.
Units Produced Per Hour
In manufacturing, a common productivity metric is the number of units produced per hour. This measures how efficiently employees convert labor hours into tangible products, something which is known as manufacturing productivity.
Formula:

Example:
If a worker produces 500 units over 40 hours:
Productivity = 500 units / 40 Hours = 12.5 units/hour.
Defect Rates
Quality is as crucial as quantity in manufacturing. Defect rates measure the percentage of products that fail to meet quality standards, impacting overall productivity.
Formula:

Example:
If 20 out of 1000 units are defective
Defect Rate = (20 / 1000) x 100 = 2%
Lower Defect Rates indicate higher productivity, as less time and resources are spent on rework.
Billable Hours
In professional services, such as consulting or law firms, productivity is often measured by calculating billable hours — the hours worked that are directly chargeable to clients.
Formula:

Example:
If an employee works 50 hours in a week, with 40 hours being billable:
Billable Hours Ratio = (40 / 50) x 100 = 80%
A higher ratio signifies greater productivity and profitability.
Project Completion Rates
Timely project completion is vital in professional services. Measuring the rate at which projects are completed on schedule reflects productivity and efficiency.
Formula:

Example:
If 18 out of 20 projects are completed on time in a quarter:
On-Time Completion Rate = (18 / 20) x 100 = 90%
High on-time completion rates enhance client satisfaction and repeat business.
Time Tracking
For remote teams, monitoring the actual time spent on tasks helps calculate productivity. The best time tracking apps can record active working hours, providing data for analysis.
Formula:

Example:
If an employee logs 40 hours in a week, with 35 hours actively working:
Productive Time Ratio = (35/ 40) x 100 = 87.5%
This ratio helps identify time management efficiency.
Output Measurement
Evaluating the quantity and quality of completed tasks is essential for remote teams. This includes assessing task completion rates and adherence to deadlines.
Formula:

Example:
If an employee is assigned 10 tasks in a week and completes 9:
Task Completion Rate = (9 / 10) x 100 = 90%
High completion rates indicate effective task management and productivity.
Thus, we can say that productivity metrics must be custom-made to industry-specific activities and goals. By employing relevant formulas for measuring productivity and consistently monitoring these metrics, organizations can enhance efficiency, maintain quality, and achieve strategic objectives.
Measuring employee productivity goes beyond simple output numbers. Several key factors must be considered to ensure a well-rounded evaluation.
High productivity is meaningless if work quality suffers. Employees who produce high volumes but compromise on accuracy or effectiveness may not be truly productive. Assess quality through customer feedback, error rates, or peer evaluations.
A productive employee should consistently complete assigned tasks within the expected timeframe. Tracking the number of completed tasks versus assigned ones helps gauge efficiency.
Setting clear performance goals allows for objective measurement. Employees who regularly meet or exceed their targets demonstrate high productivity. Consider using SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) goals for better assessments.
Time management is crucial in productivity measurement. An employee who spends excessive time on simple tasks may not be working efficiently. Tools like Clockdiary can provide insights into how work hours are utilized.
Meeting deadlines is a strong indicator of an employee’s ability to manage tasks efficiently. Frequent delays can signal productivity issues, inefficiencies, or workload mismanagement.
For roles tied to sales or production, measuring revenue per employee is an effective way to calculate productivity per employee and thereby gauge contributions to business success.
Finally, productivity should align with organizational goals. An employee may be busy, but if their work doesn’t contribute to business objectives, their efforts may not be truly productive.
By considering these factors, businesses can calculate productivity of an employee holistically, leading to better performance management and workforce optimization.
As workplaces evolve, so do the methods for calculating productivity of an employee. Companies are shifting toward data-driven, employee-centric approaches to enhance efficiency while maintaining engagement and well-being.
Traditional productivity metrics often overlook employee satisfaction. The Employee Net Promoter Score (eNPS) is gaining traction as a key metric. It measures how likely employees are to recommend their workplace, providing insight into engagement levels. Higher engagement is linked to increased productivity and lower turnover rates.
Organizations are leveraging AI-driven analytics, project management tools, and time-tracking software to monitor performance instantly. Platforms like Clockdiary help track completed tasks, collaboration efficiency, and roadblocks in real-time. This allows managers to provide proactive support rather than reactive intervention.
Annual performance reviews are becoming outdated. Instead, companies are embracing continuous feedback mechanisms through regular check-ins, peer reviews, and 360-degree feedback. This ongoing approach enables employees to adjust and improve performance dynamically, boosting overall productivity.
Rather than just tracking work output, businesses are analyzing capacity utilization—how effectively employees use their available working hours. This helps organizations optimize workloads, prevent burnout, and ensure talent is used efficiently.
Revenue per employee remains a vital productivity indicator. By dividing total revenue by the number of employees, businesses gain a clear view of workforce efficiency and profitability, allowing for better resource allocation and performance improvement strategies.
By adopting these emerging trends, companies can create a more holistic and effective approach to calculate productivity of an employee, ensuring both employee satisfaction and business success.
Clockdiary is a powerful and user-friendly time-tracking tool that helps businesses measure employee productivity with precision. Whether managing employees working from home or in-office employees, Clockdiary provides real-time insights into work hours, efficiency, and overall performance.
Let’s take a look at the key features of Clockdiary that make it ideal for calculating productivity of an employee:
Employees can log hours manually or use the automatic time recorder to track how much time they spend on tasks.
Managers can assign tasks and monitor how long employees take to complete them, ensuring workload distribution is efficient.
Clockdiary’s AI-driven rule engine analyzes work patterns and detects inefficiencies, helping managers make data-driven productivity improvements.
Generate detailed reports that analyze work patterns, task completion rates, and time spent on specific projects.
Ideal for professional service firms, Clockdiary allows businesses to track billable and non-billable hours, ensuring accurate client invoicing and revenue tracking.
Employees can submit weekly timesheets for approval, making it easy for managers to review work hours and productivity.
This feature provides automatic insights based on employees’ screen activity, identifying productivity trends and potential distractions.
The app alerts users when they’ve been inactive for a period. It also features an “activity index” helping track actual productive time versus distractions.
Clockdiary integrates seamlessly with project management platforms like Slack, Trello, and Jira, streamlining workflow tracking.
Managers can distribute tasks based on real-time data, preventing overworking some employees while underutilizing others.
By leveraging Clockdiary’s features, businesses can gain valuable insights into employee productivity, improve efficiency, and make data-driven decisions to enhance overall performance. Get in touch with us to integrate this technological wizardry into your organization and see the difference for yourself.

Frequently Asked Questions:
To calculate employee productivity in Excel, use the formula Productivity = Output ÷ Input, where “Output” represents completed tasks, sales, or revenue, and “Input” includes hours worked or resources used.
You can automate calculations using built-in Excel formulas like =A2 / B2 to divide total output by total input and visualize productivity trends with charts and conditional formatting.
HR measures employee productivity using key metrics such as task completion rates, revenue per employee, billable hours, and adherence to deadlines to assess efficiency and performance.
They also leverage tools like 360-degree feedback, self-assessments, and AI-powered time-tracking software like Clockdiary to gain deeper insights into work quality, engagement, and overall contribution to business goals.
The Employee Productivity Ratio measures workplace efficiency by comparing output (such as revenue, completed tasks, or units produced) to input (such as hours worked or resources used). It is typically calculated using the formula:
Productivity Ratio = (Total Output / Total Input) x 100,
expressed as a percentage to indicate how effectively employees contribute to organizational goals.