Struggling to calculate hours worked for your employees? You’re not alone! Accurately tracking working hours is vital for fair compensation, maintaining productivity, and efficient project management. But how do you ensure accuracy when calculating employee hours on a daily, weekly, or monthly basis?
In this article, we’ll break down everything you need to know about calculating total hours worked—from understanding what qualifies as work hours to why it’s so important to track them. Plus, we’ll guide you through using a work hours calculator to make this task a breeze. Ready to learn more? Let’s get started!
What Are Working Hours?
Working hours refer to the time an employee spends on duty, whether on office premises or remotely. It is the total time employees need to invest in work-related tasks every working day, decided at the time of employment. It does not consider any overtime worked by exempt employees.
We want to point out here that it is mandatory under law to keep a record of employee working hours for both hourly and salaried employees. This includes hours worked per day, check-in and check-out times, break times, overtime., wages paid, and other conditions of employment.
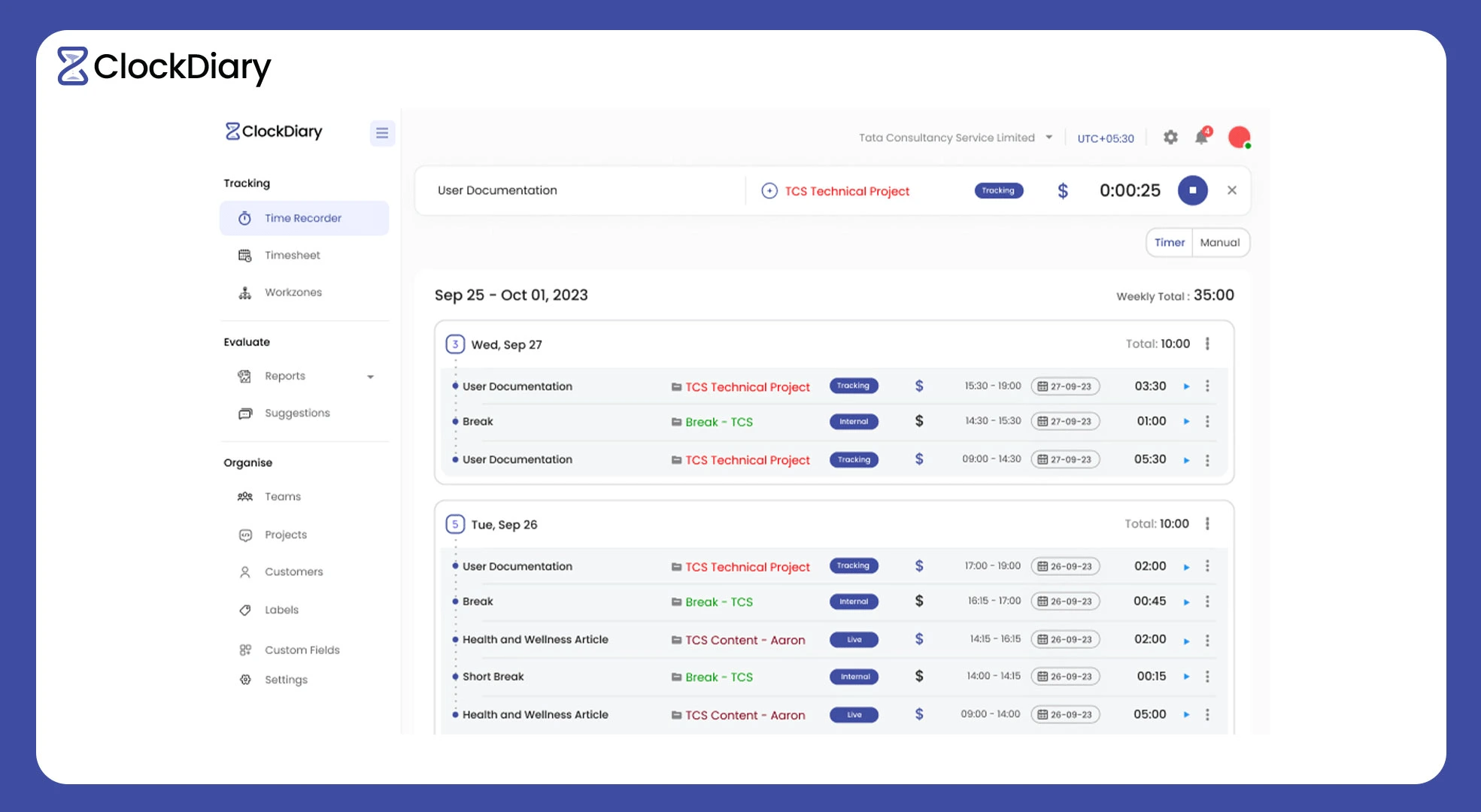
“We are more than happy to inform you that our supremely engineered working hours calculator has been implemented by more than 50 US businesses to track employee working hours. Now, you may be thinking, what is the significance of calculating work hours? Well, our next section deals with just that.”
Why is it Important to Calculate Work Hours?
Accurately calculating hours worked has become critical to ensuring seamless business operations. Whether you own a small startup or manage a large corporation, understanding how much time workers invest in specific tasks is crucial. Here are some powerful reasons for why knowing how to calculate work hours is essential:
Accurate Payroll
One of the prime reasons behind calculating work hours is to ensure payroll accuracy. Employees must receive fair compensation for their work hours; any discrepancies can cause dissatisfaction.
Once you track work hours intensively, you can ensure workers are paid appropriately for their Time, including overtime. This also boosts employee trust and morale while ensuring compliance with labor laws.
Productivity Management
Work hours calculator is necessary for anyone looking to boost productivity in their business operations. Once you track the time employees spend on different tasks, you can figure out the processes that are running smoothly and the ones that demand improvement.
Once you gain insights into the productivity levels, you can optimize workflows, allocate resources more effectively, and set realistic goals. Such a data-driven approach will help achieve better results and improve the overall performance of your company.
Project Management
Accurate tracking of work hours goes a long way in effective project management. As a manager, if you can monitor employees’ Time for different tasks and projects, you can plan and allocate resources more effectively and efficiently, ensuring projects stay within budget and on schedule.
This helps recognize potential hindrances early, providing ample Time for timely adjustments. Thus, accurate work-hour tracking is the key to successful project execution and delivery.
How to Calculate Hours Worked?
If you want to boost productivity, manage projects more effectively, and ensure fair compensation for your staff, knowing how to calculate hours worked is essential. This helps streamline operations and maintain transparency. Now, let’s dive into a step-by-step guide on how to calculate total hours worked effectively.
Step 1: Record Start And End Times
First, you should record each working day’s clock-in and clock-out times. You can record it on paper, use a spreadsheet or a work hours calculator.
Example: An employee clocks in at 9:00 AM and clocks out at 5:00 PM
| Formula:Total Time = Clock-Out Time – Clock-In Time Example Calculation:5:00 PM – 9:00 AM = 8 hours |
Step 2: Include and Subtract Breaks
Once you know the start and end times, you must consider any breaks during working hours. Breaks include lunch, tea breaks, or any other period where work is paused. It would help to subtract these break times from the total hours to ensure that only actual working hours are calculated.
Example: The employee takes a 1-hour lunch break from 1:00 PM to 2:00 PM.
| Formula:Net Hours Worked = Total Time – Break Duration Example Calculation:8 hours – 1 hour = 7 hours |
Step 3: Total Work Daily Hours
Now, that you have deducted the breaks, add the total hours worked each day. In this way, you can get the total daily hours for each worker.
Example: The employee works 7 hours (after deducting breaks) on Monday, Tuesday, and Wednesday.
| Formula: Daily Total = Net Hours Worked per Day Example Calculation: Monday: 7 hours. Tuesday: 7 hours. Wednesday: 7 hours. Daily Total for Each Day = 7 hours. |
Step 4: Weekly Work Hours Calculation
If you need to calculate full-time employee hours per week, add the daily hours worked throughout the week. This total will give you a clear picture of the total number of hours a worker has worked over a workweek.
Example: Daily hours are Monday: 7, Tuesday: 7, Wednesday: 7, Thursday: 6, and Friday: 8.
| Formula: Weekly Total = Sum of Daily Total Hours Example Calculation: 7 + 7 + 7 + 6 + 8 = 35 hours. |
Step 5: Adjust for Overtime
If any worker works more than the regular working hours in a week, these additional hours should be considered overtime. Overtime payments are generally high, so it’s essential to differentiate them from regular working hours. You must calculate overtime hours separately and make necessary changes to the payroll calculation.
Example: The regular weekly working hours are 35, but the employee works an additional 5 hours on Saturday.
| Overtime Hours = Total Weekly Hours – Regular Weekly Hours Example Calculation:40 hours – 35 hours = 5 overtime hours |
Step 6: Verify and Document
The final step is to verify all recorded hours for accuracy and document them appropriately. Double-checking calculations helps prevent errors that could lead to payroll discrepancies. Proper documentation aids in audits and resolves any disputes regarding work hours.
| Documentation Tip: Use a digital tool or spreadsheet to log these hours and include time stamps, notes for break durations, and verified signatures if necessary. |
How to Calculate Average Hours Worked Per Week?
To gain valuable insights into your employees’ work habits and time management, consider calculating full-time employee hours per week using a smart job hours calculator tool. This tool can simplify the process and help you accurately calculate hours worked. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to calculate hours worked effortlessly.
Collect Weekly Data
The first step in calculating the average hours worked per week is to gather data. You should keep track of the number of hours your employee worked in a week. A notebook, a spreadsheet, or a job hours calculator can come in handy here.
It would help if you considered all working days a week, including any overtime or extra hours worked on weekends. Error-free and consistent data collection is extremely important for an accurate calculation.
Example: An employee works the following hours in one week:
Monday: 7 hours, Tuesday: 8 hours, Wednesday: 6 hours, Thursday: 8 hours, Friday: 7 hours, Saturday: 4 hours, Sunday: 0 hours.
| Formula: Daily Work Hours = Clock-Out Time – Clock-In Time – Break Time Example Calculation for Monday: (9:00 AM – 5:00 PM) – 1-hour break = (8 – 1)= 7 hours |
Sum Total Hours
Once you have the complete weekly data, the next step is to add the total hours worked. All you need to do is sum up the hours for every working day in a week, and you will get the weekly total.
Example:
Add up the hours worked across the week:
Monday: 7 hours
Tuesday: 8 hours
Wednesday: 6 hours
Thursday: 8 hours
Friday: 7 hours
Saturday: 4 hours
| Formula: Weekly Total Hours = Sum of Daily Hours Example Calculation:7 + 8 + 6 + 8 + 7 + 4 = 40 hours |
Count Weeks
You need to calculate the total number of weeks recorded in the data set. This is an easy but crucial step. For instance, if you have kept a record of hours for four total weeks, your count will be four.
Example: You have recorded work hours for 4 weeks:
Week 1: 42 hours
Week 2: 38 hours
Week 3: 40 hours
Week 4: 40 hours
| Formula: Total Weeks = Number of Weekly Data Sets Example Calculation:4 weeks |
Calculate Average
Finally, you can calculate the average full-time employee hours per week by dividing the sum of total work hours by the total number of weeks.
Example: Total hours worked in 4 weeks = 42 + 38 + 40 + 40 = 160 hours
Total weeks = 4
| Formula: Average Weekly Hours = Total Hours Worked ÷ Total Weeks Example Calculation:160 ÷ 4 = 40 hours per week |