

How many working days are actually in a month? For employers, understanding this number is crucial for planning, budgeting, and managing employee workload effectively. According to recent labor statistics, the average month in the U.S. has around 20-22 working days, varying with weekends and public holidays.
But beyond the numbers, there’s more to consider: seasonality, industry needs, and specific state regulations can impact how many working days are in a month and, thus, your team’s availability. For employers, knowing the exact count of working days each month can make all the difference in setting realistic goals and optimizing team performance.
| Quick Summary: How many working days are in a month? It’s a question with more than one answer—depending on your country, industry, work schedule, and public holidays. In this comprehensive guide, we break down the concept of working days, working hours, and the differences between standard and flexible work arrangements like shift work, part-time, and the traditional 9-to-5. You’ll also learn how to calculate working days accurately, track productivity using modern time-tracking tools, and make smarter decisions whether you’re managing a team, planning a project, or analyzing payroll. |
Today, we will take a look at what is actually meant by a working day, a working week, and a working month, the number of average working days in a month, year, and leap year, factors affecting the number of working days, and more. So, with the primary aim to streamline business operations, let’s start.
A working day is any day when employees are typically expected to work, usually falling on weekdays—Monday through Friday—excluding weekends and public holidays. In most countries, a standard working day spans 8 hours, making up a 40-hour workweek.
Working days are essential for calculating wages, leave balances, and project timelines, as they determine the days when business operations are active. However, the concept of a working day may vary based on industry and country. For instance, some businesses operate on Saturdays or Sundays, while others might follow alternative workweeks, affecting the traditional notion of a “working day.”
In a standard workday, employees typically work 8 hours. This 8-hour day is the norm in many countries, including the US, forming the foundation of a 40-hour workweek spread across five days, Monday through Friday.
These hours are often divided into two four-hour blocks with a lunch break in between. However, variations exist depending on the industry, country, and company policies. For instance, some workplaces may adopt a shorter workday, such as 7 or even 6 hours, in pursuit of better work-life balance. Additionally, flexible schedules and remote work arrangements have introduced more diversity in what a “standard” workday means today.
Now, let’s see how work hours vary in different US states:
A working week, or workweek, typically refers to the standard number of days and hours people work in a week. In many countries, including the United States, it spans Monday to Friday, covering about 40 hours, often 8 hours daily.
The Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) in the U.S. defines a workweek as 168 hours or seven consecutive 24-hour periods, which can vary depending on company policy or labor contracts. Globally, workweeks vary: some countries have shorter workweeks, while others include Saturdays, particularly in the retail, healthcare, and hospitality sectors.
A standard full-time workweek typically consists of 40 hours, assuming an eight-hour workday across five days. This is based on the standard schedule of Monday through Friday, with weekends off.
However, some industries and jobs may require different schedules, such as longer shifts or irregular hours. In certain cases, part-time positions may involve fewer hours, while overtime work can push the weekly total beyond 40 hours. It’s important to note that the number of working hours may vary depending on national labor laws, company policies, and the type of work being performed.
Knowing the method of calculating working days is something you just can’t overlook while figuring out how many working days in a month to streamline business operations and improve productivity. Here, we would like to point out that calculating business days can vary based on types of work schedules. Here’s how to approach it for different scenarios:
For a standard full-time employee, working days are calculated based on the usual workweek, typically 5 days a week (Monday to Friday), excluding weekends and public holidays. Here’s how to do it:
| Total working days = Total calendar days – (Weekends + Public Holidays) |
Suppose an employee is working in a month with 30 days. If there are 8 weekend days and 2 public holidays, the working days are:
| 30 days – (8 weekend days + 2 holidays) = 20 working days |
Part-time employees typically work fewer hours per week than full-time employees. The calculation of their working days depends on how many hours they work each day. Here’s the formula:
| Total working days = (Total hours worked per week ÷ Number of hours worked per day) |
Example: If a part-time employee works 3 days a week, with each day consisting of 5 hours, they would have 12 working days (3 days a week X 4 weeks) in a 4-week month.
For employees working on a shift schedule, including night / third shifts or rotating shifts, the calculation can be more complex. Shift workers may have varying schedules that don’t necessarily follow a 9-to-5 workday. Here’s how to calculate working days in shift work:
| Total working days = (Total shifts worked ÷ Shifts per day) |
Example: If a shift worker works 12-hour shifts and is scheduled for 6 shifts a week, they would have 6 working days in that week, regardless of whether the shifts fall on weekdays or weekends.
Flexible work schedules allow employees to work outside the standard office hours, such as working from home or shifting hours based on personal preference. Calculating working days in flex work schedules typically depends on the agreed-upon weekly hours.
| Total working days = (Total agreed-upon hours per week ÷ Hours worked per day) |
Example: A flexible worker with an agreement to work 30 hours a week and working 6 hours per day would have 5 working days per week.
The traditional 9-to-5 workday (8 hours per day) is the most common model. For those working this schedule, the calculation is straightforward.
| Total working days = Total hours worked ÷ 8 (hours per day) |
Example: If an employee works 160 hours a month, they would have 20 working days in a standard 9-to-5 workday setup (160 ÷ 8 = 20 days).
In some cases, especially for industries like healthcare or manufacturing, employees may be required to work a full 24-hour period on a rotating or on-call basis. In such a case, the formula to calculate working days goes something like this:
| Total working days = (Total 24-hour periods worked ÷ 1 day) |
Example: If an employee works 5 entire 24-hour shifts in a month, they have worked 5 working days in that particular month.
When discussing “how many working days are in a month, ” an idea of calculating work hours or scheduling is a must. This is where two terms come into the picture: Working Week and Calendar Week. These two concepts may seem similar but are quite different. Here’s how they differ from each other:
| Aspect | Working Week | Calendar Week |
| Definition | The “Working Week” refers to the days typically considered as working days in a week, usually Monday to Friday, excluding weekends and public holidays. | The “Calendar Week” refers to the standard seven days of a week, starting from Sunday and ending on Saturday, regardless of whether they are workdays or not. |
| Length | 5 working days, excluding weekends (Saturday and Sunday) and public holidays | 7 days, from Sunday to Saturday. |
| Standard Hours | Generally consists of 40 hours (8 hours per day, 5 days). It may vary depending on the industry and company. | Does not directly relate to working hours. It’s simply the entire 7-day span of the week. |
| Focus | Focuses on the hours of productivity and work performed by employees. | Focuses on the full range of days, including non-working days like weekends. |
| Usage in Scheduling | Used for planning work tasks, team schedules, and project deadlines. | Used for personal and general timekeeping, like planning holidays or appointments. |
| Flexibility | Often flexible in some industries, where work may be done over weekends or outside typical 9-5 hours. | Fixed, with no adjustments made for individual work schedules. |
| Example | A typical 9 AM to 5 PM job follows a working week from Monday to Friday, often with weekends off. | A calendar week could be from Sunday, November 10 to Saturday, November 16, irrespective of whether the person works during the weekend. |
A working month refers to the period during which an employee is actively engaged in their job, typically aligned with a calendar month. It generally consists of business days, excluding weekends and public holidays. The exact number of working days varies depending on the country, workplace policies, and the specific month.
A standard working month often assumes a five-day workweek, resulting in approximately 20–22 working days. In employment or payroll contexts, the term may be used to calculate wages, assess productivity, or define contractual obligations. It serves as a standardized time frame for measuring professional activity and compensation.
The number of working hours in a month depends on the standard workweek and the number of working days. In many countries, a typical full-time schedule assumes 40 hours per week, with five eight-hour workdays. A month generally has around 20 to 22 working days, leading to approximately 160 to 176 working hours.
However, variations can occur due to public holidays, company policies, or part-time schedules. For payroll calculations, employers often use an average of 173.33 hours per month (based on 40 hours per week multiplied by 52 weeks and divided by 12 months). Specific hours may differ by region.
When discussing “how many working days are in a month,” two terms often arise: working month and calendar month. Though they might sound similar, they have distinct meanings and implications for businesses and employees. The following table highlights their key differences:
| Aspect | Working Month | Calendar Month |
| Definition | Refers to business days within a month, excluding weekends and holidays. | Refers to the entire duration of a month (e.g., January 1–31). |
| Number of Days | Varies based on weekends and public holidays; typically 20–22 days. | Fixed between 28 and 31 days, depending on the month. |
| Work Hours | Based on the number of working days, usually 160–176 hours for full-time employees. | Includes all 24-hour days in the month, irrespective of work. |
| Purpose | Used for payroll calculations, project timelines, and productivity assessments. | Used for scheduling, record-keeping, and official deadlines. |
| Flexibility | Changes with public holidays and organizational policies. | Fixed and universal across all contexts. |
| Relevance to Employees | Focuses on actual days worked, affecting salaries and leave tracking. | Broadly relevant for understanding contractual obligations. |
Thus, we can say that a working month aligns more closely with an employee’s professional activities, excluding non-working days. Speaking about standardization, a calendar month provides a universally fixed period, while a working month varies depending on external factors. Employers and HR departments often rely on the working month for accurate salary calculations, while a calendar month serves broader administrative needs.
Understanding these differences helps employers and employees set clearer expectations and manage time effectively in professional settings.
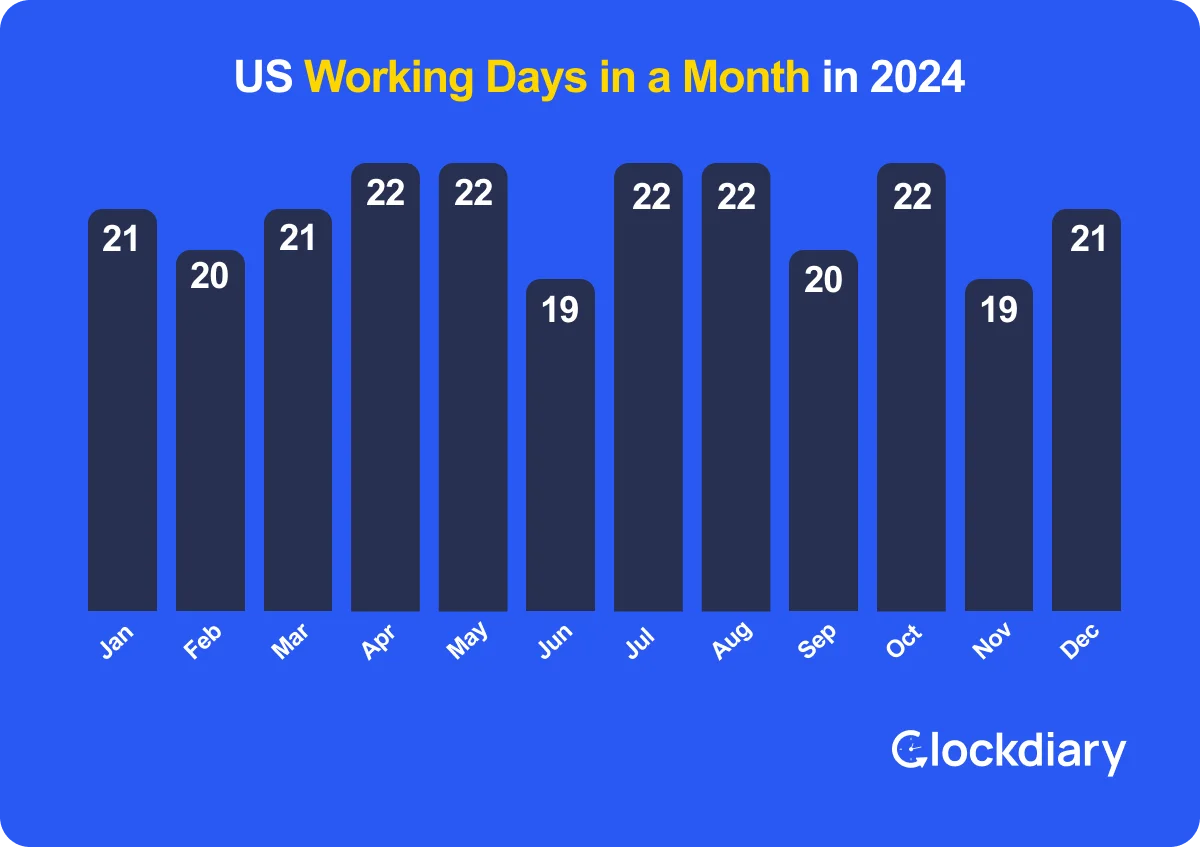
The number of working days in a month varies depending on the calendar, weekends, and public holidays. In a typical five-day workweek system, a month generally includes between 20 to 22 working days. Months with 31 days, like January or August, often have 22 working days, while shorter months, like February, may have around 20.
Public holidays can further reduce this number. Employers use these figures to calculate wages, project timelines, or leave balances. For example, a month with two public holidays may have 18 to 20 working days. Regional differences and workplace policies also impact the total count.
The number of working days in a year typically ranges from 250 to 260, assuming a standard five-day workweek. This is calculated by subtracting weekends (104 days) from the total 365 days a year.
Public holidays can reduce this number further, depending on the country and organization’s holiday policy. In some countries, employees may receive 10 to 15 public holidays, bringing the total business days closer to 240–250. Companies with different work schedules, such as a four-day workweek or those operating in regions with more holidays, may have fewer business days in a year.
Consider maintaining a team-wide calendar to keep track of business days. All you need to do is add each team member to a shared platform like Google Calendar and ask them to add their time off and local holidays so that you can plan accordingly.
You can integrate Google Calendar with a time-tracking tool like Clockdiary to streamline work hours tracking and payroll. Clockdiary is also ideal for automating:
If you are having trouble manually calculating pay periods, reduce time wastage, frustration, and chances of error by giving Clockdiary a try, free for up to 10 users.

A leap year has 366 days, compared to the standard 365 days. With a typical five-day workweek, weekends (Saturdays and Sundays) account for 104 days, leaving (366 – 104) = 262 days for work, provided the extra day falls on weekdays like Monday.
However, public holidays can further reduce the number of working days. If a country or organization observes 10 to 15 public holidays, this number might decrease to around 247 to 252 working days. The exact count depends on the specific holidays and the work schedule of the individual or company. In summary, a leap year typically contains between 247 and 262 working days, depending on local factors.
While discussing “How many working days are in a month?”, we would like to point out that this number in a particular year or month isn’t a fixed figure; it varies based on several factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for employers, employees, and organizations to manage time effectively. Here’s an in-depth look at the key variables:
The United States recognizes 11 federal public holidays, such as Independence Day, Thanksgiving, and Christmas. However, these holidays do not always translate into days off for everyone. For example, retail and healthcare workers often work during holidays to meet consumer demands.
Additionally, states and local governments can designate their own holidays, further affecting the number of business days. For instance, Massachusetts celebrates Patriots’ Day, while Texas observes Texas Independence Day, potentially reducing working days for residents in these states. Companies also have discretion in observing these holidays, leading to variability across workplaces.
Employee absences significantly affect the number of working days. Sick leave policies, which vary by employer and state, play a crucial role. While the federal government does not mandate paid sick leave, many states, such as California and New York, require employers to provide it.
Personal leave, including vacation days, parental leave, and bereavement leave, also impacts working days. For example, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics reports that full-time employees typically receive an average of 10 to 14 paid vacation days annually after one year of service. Additionally, unplanned absences, such as those due to severe weather or family emergencies, can further reduce the number of days an individual works in a year.
Working days can vary significantly across industries. Retail, hospitality, and healthcare often require employees to work weekends and holidays, increasing their total working days. On the flip side, industries like education adhere to structured academic calendars, reducing the working days for teachers and staff compared to other professions.
Tech and corporate sectors may offer flexible work schedules, allowing employees to adapt their working days based on personal and organizational needs. Seasonal industries, such as agriculture or tourism, experience fluctuations in working days depending on peak activity periods.
In the end, we can say that the number of average business days in a month in the U.S. is shaped by an interplay of public holidays, leave policies, and industry-specific demands. Understanding these factors provides insight into how work schedules vary across different regions and sectors, reflecting the diverse nature of the American workforce.
In today’s quick-paced work environment, keeping track of working days and hours is essential for maximizing productivity. By understanding how you spend your time, you can identify areas for improvement, allocate resources effectively, and strike a healthy work-life balance. So, in this part of our blog, “ How many working days are in a month?” let’s see how tracking your working days can help you get more done without burning out.
Effective tracking of working days and hours is essential for optimizing productivity, ensuring accurate payroll, and managing projects. By implementing best practices, businesses can make time tracking seamless and beneficial for both employers and employees. Here are some key tips to enhance your approach:
Educate employees on the importance of time tracking and how it benefits them and the organization. Provide clear guidelines on recording time, explaining expectations, and emphasizing transparency to promote trust.
Encourage employees to log hours based on specific projects or tasks. With 49% of US employees admitting to time theft, executing this becomes that much more important. This approach not only helps track business days but also provides valuable insights into how time is allocated across projects, aiding in resource management.
Selecting the right time-tracking tool is crucial. In this context, we would like to point out that the average wage in the USA is $33.45 per hour and $1146.99 per week. So, if an employee clocks in 10 minutes late daily, and if we consider 260 business days in a year, it will lead to approximately $1450 of stolen time for a business.
Always look for user-friendly software that integrates with other systems like payroll and project management tools, and provides customizable features to meet your organization’s needs.
Establish a routine to review submitted timesheets for accuracy and completeness. Regular checks help identify inconsistencies, resolve discrepancies, and ensure compliance with company policies.
It is absolutely essential to categorize billable vs non-billable hours. Tracking both types allows businesses to evaluate productivity, manage costs, and maintain transparency with clients.
Analyze time-tracking data to identify patterns, improve workflows, and forecast future needs. Insights from this data can help streamline operations and optimize resource allocation.
Reassure employees that their data will be used responsibly. Implement policies to safeguard privacy and ensure that tracking focuses on productivity rather than micromanagement.
By implementing these strategies, businesses can monitor business days and hours effectively, thereby enhancing operational efficiency and fostering a productive work environment as well.
We are no strangers to the fact that productivity tracking tools are indispensable for businesses and individuals looking to optimize time management and streamline workflows. This is where the significance of seeking a good tool or software for productivity tracking is perceived the most. Among the many tools available, Clockdiary stands out as one of the best options for productivity tracking, offering a comprehensive suite of features designed for efficiency, flexibility, and ease of use. Let’s take a look at some of its most exquisite features:
Clockdiary allows users to track time, both manually and automatically. Whether you’re working on a specific project or multiple tasks, its intuitive interface ensures you can log hours effortlessly. The “automatic time recorder” function is perfect for those who prefer real-time tracking, while manual entries accommodate retrospective updates.
Organizing time around projects is simple with Clockdiary. You can assign tasks, categorize projects as billable and non-billable, and monitor real-time progress (thanks to its “Activity Tracker” feature, capturing screenshots at regular intervals). It also provides a clear breakdown of hours spent on different projects, helping you identify areas where efficiency can improve.
Clockdiary generates detailed reports, offering insights into productivity patterns. These reports can be customized to show billable hours, non-billable hours, or a mix of both, making it ideal for businesses that need accurate billing and time allocation.
For businesses with teams, Clockdiary simplifies tracking across multiple users, and in different time zones as well. Managers can review timesheets, approve logged hours, and ensure everyone stays aligned on project timelines.
Clockdiary is available across devices, including desktops, smartphones, and browsers. This ensures users can track productivity wherever they are, enhancing flexibility.
With a free version for up to 10 users packed with robust features and affordable paid plans priced at $2.99 per user per month and $29.99 per user per year (free for 2 months) with additional functionalities like AI-powered smart assistant, priority ticket handling, 24/7 customer support and more, Clockdiary is suitable for both individuals and organizations.
Clockdiary combines simplicity, versatility, and powerful analytics, making it the go-to tool for productivity tracking. Its extensive features empower users to maximize their time and achieve better results, whether for personal projects or team-based initiatives.
Understanding the relationship between the number of working days and productivity metrics is crucial for businesses striving to optimize performance. Below is a detailed comparison highlighting key differences and the factors influencing both:
| Aspect | Working Days | Productivity Metrics |
| Definition | Refers to the number of days employees are scheduled to work annually, excluding holidays and leaves. | Quantitative and qualitative measures of an employee’s or team’s output. |
| Focus | Time-based measure focusing on attendance. | Output-based measure focusing on results and efficiency. |
| Key Influencers | Public holidays, sick leaves, vacation days, and industry norms. | Tools, processes, skills, and time management practices. |
| Measurement Tools | Calendars, payroll systems, and time-tracking software | Performance management software, project tracking tools, and KPIs. |
| Impact on Operations | Determines resource availability for scheduling and planning. | Drives decision-making around performance improvement strategies. |
| Correlation | High working days do not always equate to high productivity. | High productivity can often be achieved with optimized working days |
| Industry Variations | Fixed in industries like education; variable in seasonal jobs. | Dependent on industry-specific KPIs like sales, output, or customer satisfaction. |
| Employee Perspective | Can be seen as an indicator of workload and work-life balance. | Reflects individual and team contributions and achievements. |
| Management Strategy | Plan schedules to maximize availability without burnout. | Implement tools and techniques to improve efficiency and outcomes. |
Thus, we can say that while working days provide a framework for availability, productivity metrics measure the actual value delivered during those days. Balancing both by focusing on efficient work practices rather than simply increasing workdays ensures better results and employee satisfaction as well.
Conclusion
So, by now, you know that a month has 20-22 working days after considering weekends, public holidays, and the industry’s operational schedule. If you happen to run a business, you should plan and communicate public holidays in advance, thus ensuring your team has a proper understanding of their workdays.
This planning will not just help your business and employees improve time management but optimize resource allocation as well. However, if you want to take your time management skills to the next level, consider investing in a smart employee time-tracking software like ClockDiary. The reports this software generates can help you know when and for how long your staff members are working. Fill out this form to connect with us and stay informed about your employees’ working and non-working days anytime, every time.

FAQs:
The number of working days in February depends on the year and the specific calendar, but typically, there are 20 to 22 working days. In a common year, February has 20 working days, and in a leap year, it may have 21 or 22, depending on when weekends and public holidays fall.
Leap years add an extra day (February 29) to the calendar, which can increase the number of working days depending on where it falls in the week. If the extra day is a weekday, it adds one more working day to that year. That is, that particular year has 261 business days. Otherwise, it does not impact the count, and the number of working days remains at 260.
Public holidays are generally not considered working days, as most employees have the day off. However, in some industries or job roles, employees may still be required to work on public holidays, and in those cases, the holiday may be compensated differently.