

Ever wondered how to accurately measure your team’s workload, especially when dealing with both full-time and part-time staff? Understanding Full-Time Equivalent (FTE) is crucial for effective resource planning, budgeting, and compliance.
For instance, under the Affordable Care Act (ACA), businesses with 50 or more FTEs are required to provide health insurance benefits. Accurate FTE calculations help ensure compliance with such regulations.
Moreover, FTE comes in handy to determine labor costs and optimize workforce management. In this guide, we’ll demystify FTE meaning, walk you through its calculation, and provide real-world examples to help you apply it effectively in your organization. So, let’s begin.
| Quick Summary: Full Time Equivalent (FTE) is a crucial metric that helps businesses understand workforce capacity by converting part-time and full-time hours into a standardized unit. Whether you’re managing staffing, planning budgets, or ensuring legal compliance, accurate FTE calculation supports smarter decisions across HR, finance, and operations. This blog offers a complete guide with real-world examples, calculation methods, compliance insights, and practical tools like a free FTE calculator and Excel template. In this blog, you’ll discover: ⦿ What Full-Time Equivalent (FTE) means and why it matters in today’s workforce. ⦿ The step-by-step formula to calculate FTE with examples and key considerations. ⦿ Real-world FTE calculation scenarios across various business contexts. ⦿ Free, downloadable FTE calculators and Excel templates for easy implementation. template ⦿ How FTE supports budgeting, payroll, and staffing decisions across departments. ⦿ Compliance considerations under U.S. labor laws like ACA, FMLA, and FLSA. ⦿ How different industries—from healthcare to tech—use FTE for planning and reporting. |
Full-Time Equivalent (FTE) is a unit that measures an employee’s workload in a way that makes it easier to compare staffing levels across different roles and schedules. Instead of counting headcount alone, FTE expresses work hours as a proportion of a full-time schedule—typically 40 hours per week.
For example, two part-time employees working 20 hours each equal one FTE. You can track the number of hours your employees work with a good time tracking and timesheet app like Clockdiary. This metric is especially useful for HR, finance, and project managers when budgeting, forecasting, or complying with labor laws like the Affordable Care Act.
In short, FTE acronym, full-time equivalent, helps businesses understand how much full-time labor their workforce truly represents. Now that you have a clear understanding of full time equivalent meaning, let’s try to find out how to calculate full-time equivalent in the next section.
Now, that we have a clear idea of full time equivalent definition, understanding how to calculate Full Time Equivalent (FTE) is essential for workforce planning, budget forecasting, and legal compliance. Whether you’re an HR professional estimating staffing needs or a small business owner navigating ACA requirements, the FTE formula provides clarity.
| FTE = Total Hours Worked / Total Hours in A Full Time Schedule |
Usually, a full-time workweek is 40 hours, but this can vary based on your company policy or regional labor laws.

Let’s say your company has 3 employees:
Note: You need to have a clear understanding of billable vs non-billable hours comparison. Here, we have considered only billable hours.
| Total hours worked = 40 + 20 + 30 = 90 hours Standard workweek = 40 hours FTE = 90 / 40 = 2.25 FTEs |
So, your team’s workload is equivalent to 2.25 full-time equivalent employees.
Now, that you are aware of fte definition and calculation procedure, let’s look at some clear, real-world scenarios to help you better understand how to calculate Full-Time Equivalent (FTE).
Scenario 1:
A company uses a 40-hour full-time workweek.
| Total FTE: 1.0 + 0.5 + 0.25 = 1.75 FTE |
Scenario 2:
A company defines a 35-hour full-time workweek.
| Total FTE: 1.0 + 0.5 = 1.5 FTE |
Scenario 3:
A company has 3 full-time employees (40 hours each) and 2 part-time employees (20 hours each).
| Total FTE: 160 ÷ 40 = 4.0 FTE |
Scenario 4:
A company has 2 full-time employees (40 hours each) and 3 part-time employees (10 hours each).
| Total FTE: 110 ÷ 40 = 2.75 FTE |
These examples show how FTE calculations can be adapted based on different working hours and staff mixes — offering clear, practical insights for business planning and compliance.
Having a reliable Full-Time Equivalent calculator can save you hours of manual work and improve decision-making across your organization. Whether you’re managing headcount, planning budgets, or ensuring compliance, an FTE calculator helps simplify the math and boost accuracy. You can also avail of free Excel time tracking templates to make time tracking seem just like a walk in the park.
Here’s how different teams and use cases can benefit from a free FTE calc and Excel template.
Track both full-time and part-time hours in one place to calculate total FTEs company-wide. Ideal for HR, finance, and operations teams. Good timesheet apps can come in handy here.
Download the FTE Calculator for All Employees
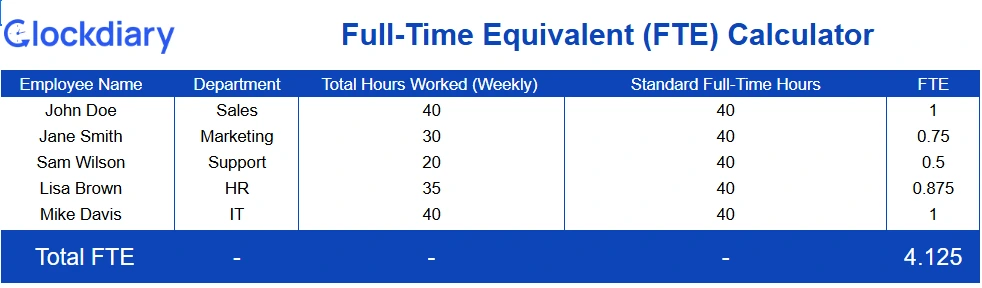
Estimate salary expenses based on FTEs rather than headcount. Great for finance teams planning payroll budgets or forecasting future labor costs.
Download the FTE Calculator for Salary Estimation
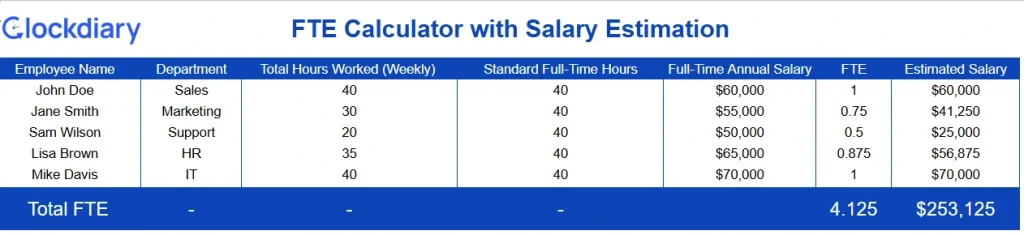
Calculate how many full-time equivalents are needed to meet project deadlines. Useful for resource allocation, scheduling, and cost control.
Download the FTE Calculator for Project Managers
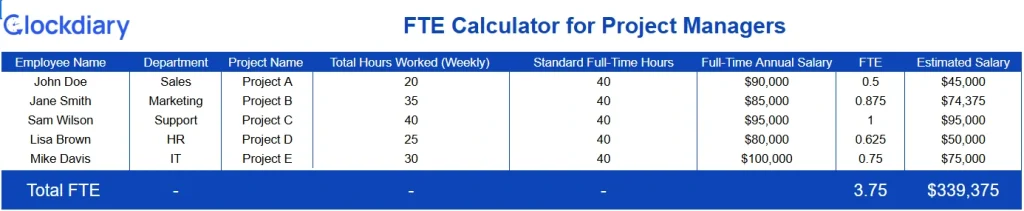
Determine FTE count to check eligibility for tax credits under programs like the Employee Retention Credit (ERC) or Work Opportunity Tax Credit (WOTC).
Download the FTE Calculator for The Small Businesses Tax Credit Program
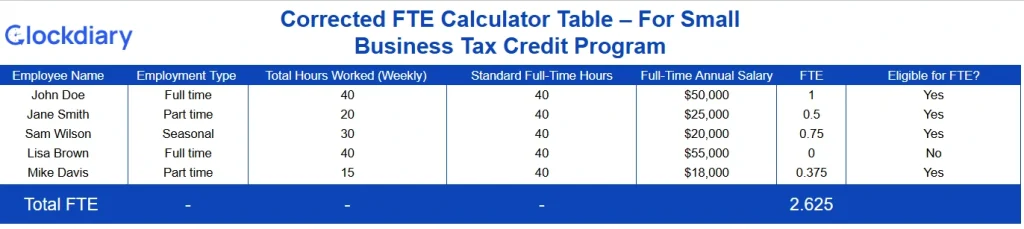
If you’re close to the 50-employee mark, use a full time equivalent calculator to see if you qualify as an ALE under the Affordable Care Act—and whether you must provide health coverage.
Download the FTE Calculator for Applicable Large Employers (ALE)
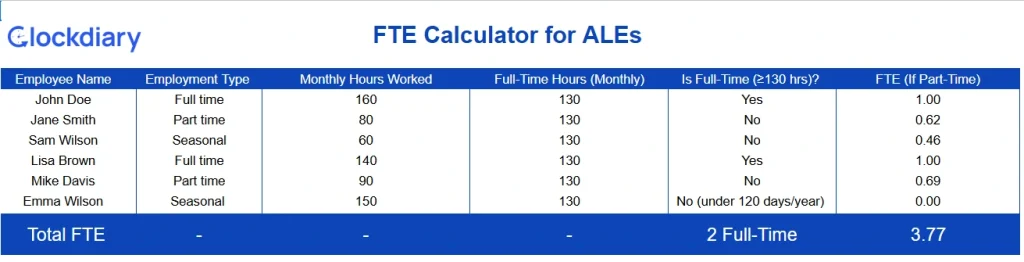
Compare available FTEs to workload demand. Helps in identifying overstaffing, burnout risks, or gaps in staffing coverage.
Download the FTE Calculator for Capacity vs Utilization Analysis
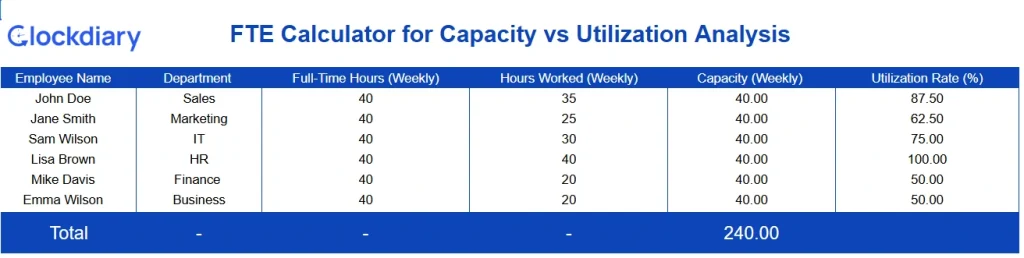
Ensure you meet FTE requirements for PPP loan forgiveness by accurately calculating average FTEs during the covered period.
Download the FTE Calculator for The Paycheck Protection Program (PPP)
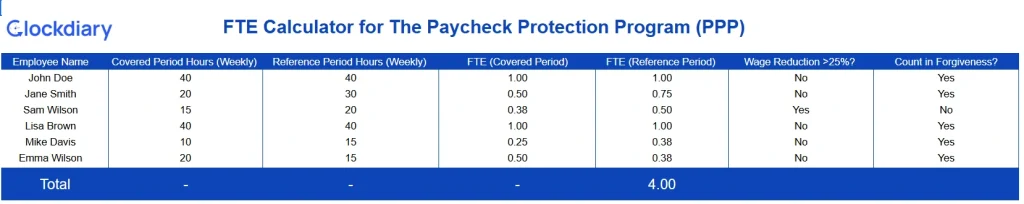
Plan future hiring needs based on projected workloads and business growth goals using simple, scalable FTE projections.
Download the FTE Calculator for Hiring Forecast (Growth Planning)
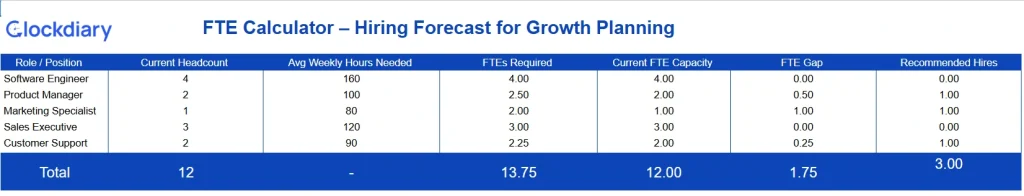
Full Time Equivalent (FTE) is more than just a headcount tool—it’s a strategic metric that supports nearly every area of business operations. Here’s why calculating FTE is so crucial:
Example: If you have 2 full-time staff (40 hrs/week) and 3 part-time staff (20 hrs/week), total hours = (2 X 40) + (3 X 20) = 140 hours.
| FTE = 140 ÷ 40 = 3.5 FTE |
Example: If a project needs 400 hours and a full-time staff works 160 hours/month,
| FTE = 400 ÷ 160 = 2.5 FTE |
Example: If your average cost per FTE is $50,000/year,
| Total Labor Cost = FTE × Average Cost= 10 × $50,000 = $500,000/year |
Example: If a company averages 52 FTEs/year, it qualifies as an ALE and must offer health insurance.
As we have already discussed meaning fte, you can well understand that it is a universal metric that plays a vital role across industries. From healthcare to tech, understanding and applying full time equivalent helps organizations optimize resources, improve staffing decisions, and ensure compliance with industry-specific regulations.
In hospitals, clinics, and other medical facilities, FTE is used to maintain safe staffing levels while controlling costs. In 2023, the U.S. healthcare sector employed over 17 million individuals, making it the nation’s largest employment sector. HR teams calculate FTE to determine how many nurses, doctors, or technicians are needed per shift to meet patient care standards.
It also helps with regulatory reporting and justifying budget allocations for grants or funding programs.
Example: A hospital might require 25 FTE nurses to maintain adequate coverage for a 24/7 emergency department.
The tech industry significantly contributes to the U.S. economy, with computer and IT jobs reporting a median annual wage of $104,420 in May 2023. Tech companies often use FTE to plan and manage teams across multiple projects. For instance, a software development firm may calculate FTEs to allocate developers, QA testers, and project managers based on sprint goals or release deadlines.
FTE also plays a role in forecasting hiring needs during growth phases or investor reporting for startups.
Example: If a mobile app project needs 3.5 FTE developers over 6 months, it could be covered by 3 full-time and 1 part-time developer, ensuring workload balance and budget control.
The global entertainment and media industry grew by 5% in 2023, reaching revenues of $2.8 trillion. In media and creative industries, teams work on a project basis with a mix of full-time staff and freelancers. Full time equivalent helps in tracking total labor resources and calculating profitability per project.
It also aids in balancing workloads among writers, editors, designers, and marketers to prevent burnout while staying within production timelines.
Example: A digital marketing agency might operate with 12 full time equivalent staffs, combining full-time, part-time, and freelance content creators to meet client demands and seasonal workload spikes.
Schools and universities use FTE to report staffing levels to state and federal authorities. For example, a school may have a mix of full-time and part-time teachers, and FTE helps standardize those figures for budgeting and compliance. For example, the library sector had the highest average number of FTE positions budgeted, with an average of 20.32 positions in 2024.
It also helps administrators assess whether current staffing meets student-teacher ratio requirements or needs adjustment.
Example: A university might calculate 30 FTE faculty positions to deliver its academic programs while balancing adjunct and part-time instructors’ schedules.
In the end we can say that no matter the industry, full time equivalent serves as a critical planning and decision-making tool that aligns workforce capacity with operational goals.
Full Time Equivalent (FTE) calculations aren’t just useful for operations—they’re also essential for staying compliant with various U.S. labor laws. Whether you’re a small business or a growing enterprise, miscalculating FTEs can lead to costly penalties and legal issues.
By understanding fte explanation and accurately calculating FTEs, employers can navigate the complexities of labor laws, avoid penalties, and ensure a compliant workplace environment.
When managing a workforce, it’s important to understand not just how many people you employ, but also how much work is actually being done. That’s where Full Time Equivalent (FTE) stands apart from other employment metrics like headcount and labor cost indicators.
| Metric | Definition | Use Case | Example |
| FTE | Measures total labor hours as a proportion of full-time hours (e.g., 1.0 FTE = 40 hours / week.) | Ideal for analyzing workload, productivity, and compliance. | 2 part-time employees working 20 hours / week each = 1.0 FTE |
| Headcount | Counts each individual employee, regardless of hours worked. | Useful for organizational structure and benefits eligibility. | 2 part-time employees = 2 headcount |
By integrating these metrics, organizations can gain a comprehensive view of their workforce, enabling data-driven decisions that enhance efficiency and profitability.
If you’re looking to simplify the process of calculating Full Time Equivalent (FTE), Clockdiary is your go-to solution. Designed with small businesses, HR teams, and project managers in mind, Clockdiary, the best time tracking app, combines powerful features with a user-friendly interface to ensure accurate, real-time tracking of employee hours.
Here’s how it can help streamline your FTE calculations:
So, in the end, we can say that with Clockdiary, you get a clear, centralized system for tracking work hours—making FTE calculations more accurate, efficient, and audit-ready. Integrate this supremely engineered time tracker into your business ecosystem to make workforce planning, staffing needs, budgeting and cost management seem like a breeze.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
FTE stands for Full Time Equivalent. It’s a metric that standardizes employee workloads by converting the total hours worked into the number of full-time employees an organization would need to perform the same amount of work.
FTE, or Full-Time Equivalent, is a unit that measures the workload of employees in a way that makes part-time and full-time workloads comparable. It helps businesses understand how many full-time workers would be needed to complete the total hours worked by all employees.
In Workday, FTE (Full Time Equivalent) represents the proportion of a full-time schedule that an employee works, based on their assigned hours. It helps organizations manage workforce planning, compensation, and compliance by standardizing workloads across part-time and full-time roles.
To calculate Full Time Equivalent (FTE) employees, divide the total number of hours worked by all employees in a given period by the number of hours in a full-time schedule. The formula is: FTE = Total Hours Worked ÷ Full-Time Hours per Period (typically 40 hours per week).
To work out a Full-Time Equivalent (FTE) salary, multiply the employee’s actual salary by the ratio of their working hours to full-time hours. The formula is: FTE Salary = (Actual Hours Worked ÷ Full-Time Hours) × Full-Time Salary.